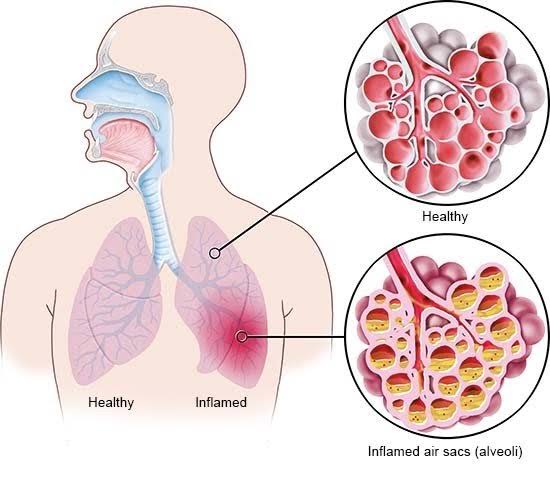
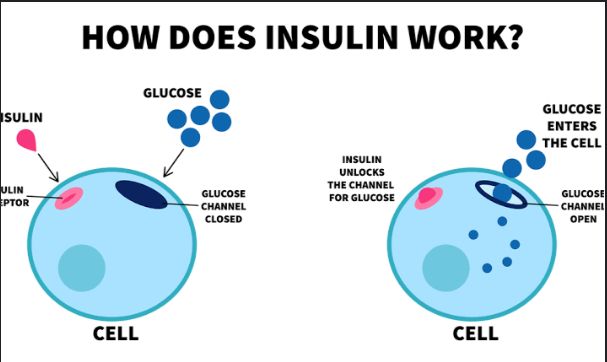
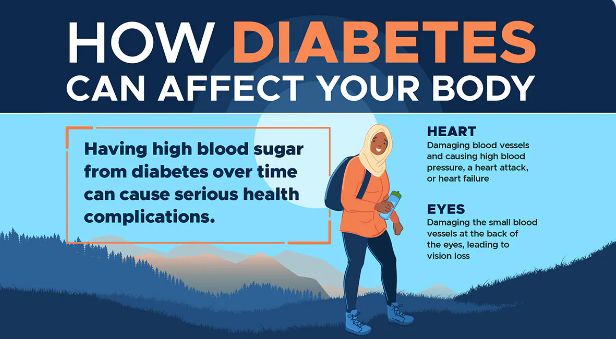
TheVaginal infections are common but can be managed effectively with the right knowledge and care especially when noticed early.
UTIs
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) can cause a range of symptoms, including a burning sensation during urination, frequent urination, and cloudy or foul-smelling urine. These infections often occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract.
To manage UTIs:
●Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps flush bacteria from the urinary tract.
●Take Antibiotics: UTIs often require antibiotics prescribed by a healthcare provider. Complete the full course to avoid recurrence.
●Good Bathroom Habits: such as wiping from front to back to prevent the spread of bacteria from the anus to the urinary tract.
●Beware of the higher risk of infection in public toilets and bathrooms.
●Yeast Infections: Yeast infections occur when there is an overgrowth of the fungus Candida. Symptoms include itching, irritation, and thick, white discharge. To manage yeast infections:
●Use Antifungal Medications: Over-the-counter antifungal creams, suppositories, or oral medications can effectively treat yeast infections.
●Avoid Scented Products: Douches, scented soaps, and feminine hygiene products can disrupt the natural pH balance of the vagina, leading to yeast overgrowth.
●Wear Breathable Underwear: Opt for cotton underwear to keep the area dry, reducing the likelihood of yeast infections.
Chlamydia
Chlamydia is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) that often presents no symptoms but can cause pelvic pain or abnormal discharge in women. If left untreated, it can lead to serious complications, including infertility.
How to Manage Chlamydia
○Get Tested Regularly: Regular STI screenings are important, especially if you are sexually active with new or multiple partners.
●Take Antibiotics: Chlamydia is treated with a course of antibiotics. Both partners should be treated to prevent reinfection.
●Use Protection: Consistent use of condoms helps prevent the spread of STI, including chlamydia.
Bacterial Vaginosis (BV)
BV occurs when there is an imbalance in the natural bacteria in the vagina, leading to symptoms like thin, gray discharge and a fishy odor.
Management of BV
○Antibiotics: BV is treated with antibiotics, either oral or topical. Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions carefully.
●Limit Douching: Douching disrupts the natural balance of bacteria and can increase the risk of BV.
●Probiotics: Incorporating probiotics into your diet may help maintain a healthy balance of vaginal bacteria.
Vaginal Hygiene Tips
Wash Gently: Clean the vaginal area with warm water and mild, unscented soap. Avoid harsh scrubbing, which can irritate the sensitive skin.
Avoid Scented Products: Scented tampons, pads, and wipes can disrupt the natural pH of the vagina, increasing the risk of infections.
Change Sanitary Products Regularly: Whether using tampons, pads, or liners, change them frequently to reduce moisture and prevent infections.
Wear Breathable Underwear: Choose cotton or moisture-wicking fabrics, and avoid tight-fitting clothing that can trap moisture and heat, creating an environment for bacteria to grow.