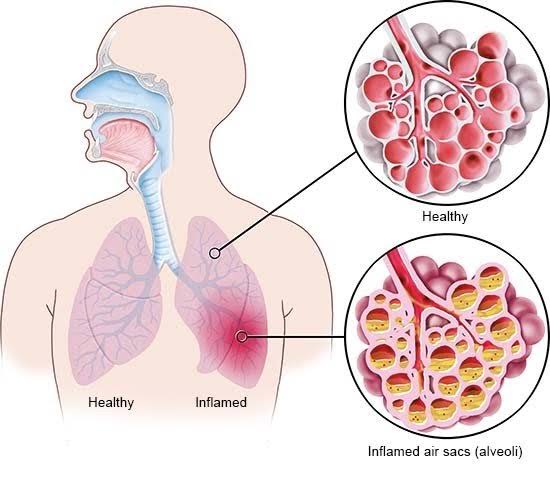
Good nutrition is about consistently choosing healthy foods and healthy eating patterns.
Healthy eating emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, dairy, and protein. Eat More Protein for Muscle Health. Plant-based and animal protein sources help strengthen muscles, aid metabolism, and promote tissue repair.
Always prefer a balanced diet.
Dairy recommendations include low-fat or fat-free milk, lactose-free milk, and fortified soy beverages. Other plant-based beverages do not have the same nutritional properties as animal's milk and soy beverages.
Protein recommendations include seafood, lean meats and poultry, eggs, legumes (beans, peas, and lentils), soy products, nuts, and seeds.
Ensure to consume less added sugar, avoid saturated fat, and take less sodium. You can do this by:
- Taking adequate fiber which helps maintain gut health and aid in digestion. Fiber also helps control blood sugar and lowers cholesterol levels. Fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds are rich in fiber.
- Increase Calcium and vitamin D intake. The minerals promote optimal bone.
- Replacing saturated fat with healthier unsaturated fats can help protect your heart. Common sources of saturated fat include fatty meats, full-fat milk and cheese, butter, avocado, cream cheese etc.
- Reduce sodium intake. Eating too much sodium can raise your risk of high blood pressure, heart attack, and stroke. Instead use herbs and natural spices rather than excessive salt intake.
- Limit added sugars. Too much added sugar in your diet can contribute to weight gain, obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease. Added sugars are sugars and syrups that are added to foods and drinks when they are processed or prepared.
Stay Hydrated. Drink at least 8 glasses of water daily to maintain hydration, support digestion, and boost energy levels. Reduce sugary drinks and excessive caffeine.
Take adequate portions of meals and avoid over eating. Its also advisable to plan your meals.
Limit Alcohol and Tobacco. Excessive alcohol and smoking increase the risk of chronic diseases like liver disease and cancer.
Consult a Nutritionist for Personalized Advice- If you have dietary restrictions or health conditions, seek guidance from a nutrition expert for a tailored meal plan.
Identifying Signs of Malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when the body does not receive enough nutrients or the right balance of nutrients for proper function.
General Signs
Unintended Weight Loss or Weight Gain – Rapid weight changes can indicate nutrient imbalances.
Fatigue and Weakness – Lack of energy due to inadequate calories and nutrients.
Frequent Illnesses and Slow Healing – Poor immune function due to vitamin and mineral deficiencies.
Dry, Flaky Skin and Hair Loss – Lack of essential vitamins like A, C, and E, and protein deficiency.
Brittle Nails – May indicate iron, protein, or biotin deficiency.
Swollen or Bleeding Gums – A sign of vitamin C deficiency (scurvy).
Poor Concentration and Memory Issues – Nutrient deficiencies, especially B vitamins, affect brain function.
Muscle Weakness and Wasting – Inadequate protein intake leads to muscle loss.
Swollen Legs or Feet (Edema) – Low protein levels can cause fluid retention.
Digestive Issues (Diarrhea, Constipation, Bloating) – Poor gut health from imbalanced nutrition.
Signs of Malnutrition in Children
Stunted Growth – Lack of proper nutrition affects height and development.
Delayed Milestones – Poor brain development and slow motor skills.
Swollen Belly (Kwashiorkor) – Due to severe protein deficiency.
Irritability and Behavioral Changes – Low blood sugar and nutrient deficiencies can affect mood.
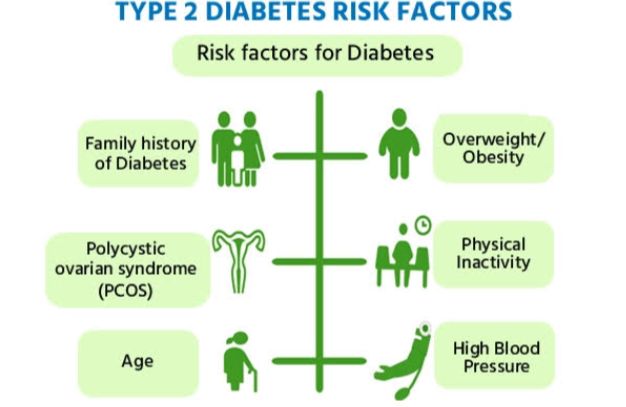
Common Risk Factors
Elderly individuals – Reduced appetite and nutrient absorption.
Pregnant and breastfeeding women – Increased nutritional demands.
People with chronic illnesses – Conditions like diabetes, cancer, and digestive disorders affect nutrient absorption.
Children and infants – Require adequate nutrients for growth and development.
Note: If you suspect malnutrition, consult a healthcare provider or nutritionist for dietary guidance and treatment.