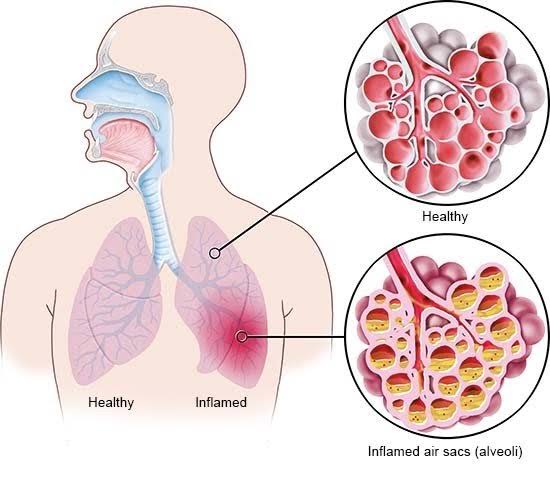
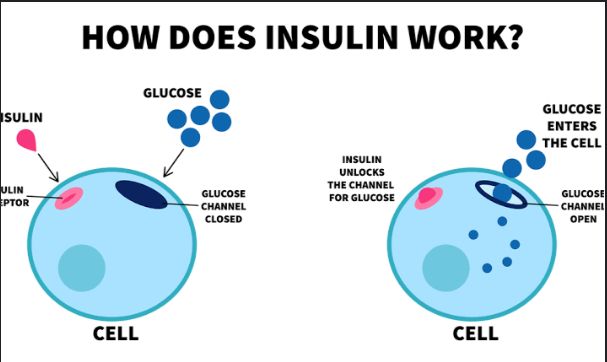
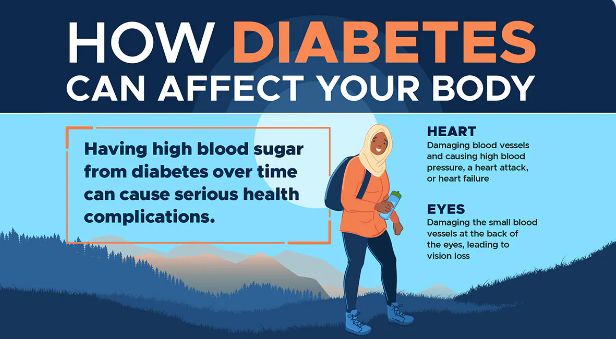
Exercise and diet are the two major ways of controlling blood pressure hence preventing, delaying or lessening the need for medication.
How Exercise aids in managing high Blood pressure.
Regular exercise helps increase your heart rate and breathing rates. With time your heart is strenghthened hence making it pump bloo with less effort. As a result, less pressure is put on your arteries.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend doing moderate-intensity exercise per week, or around 30 minutes a day, 5 days a week. For children and teens, the CDC recommend 1 hour of exercise per day.
Moderate exercise can include walking, stretching, carrying out chores or less intense work-outs.
Common activities for moderate-intense exercise include:using the stairs,walking, jogging household chores, swimming, dancing, gardening, cycling, playing a team sport.
Exercise helps manage weight gain and watch waist circumference. Since hypertension is associated with obesity and overweight, losing excess calories helps manage high blood pressure.
The Role of Diet in management of Hypertension
A healthy diet is essential to general well-being.
Always choose food that are low on saturated fat and cholesterol.
Diets rich in whole grains, fruits & vegetables, low fat dairy products are highly recommended.
Additionally, ensure you take adequate amounts of potassium in your diet. You can always inquire from your nutritionist or helathcare provider on how much potassium you need.
Be cautious on the amount of sodium you take since your body only requires a little amount of sodium. You can check this by:
- Using little amounts of table salts when preparing meals and avoid adding table salt to food.
- Limiting consumption of processed foods which may have high amounts of sodium.
- Checking food and beverage levels for amount of sodium
- Using non-salty spices to add flavor to food.
The DASH diet was developed to help manage hypertension by encouraging people to adopt healthy eating habits.
DASH stands for Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension.
It focuses on vegetables, fruits and whole grains, low fat dairy products, as well as proteins such as fish, poultry, beans and nuts.
The DASH Guideline limits salt (sodium) intake to about 2300mg/day (equivalent to 1 teaspoon or salt)
On the lower scale, it limits sodium to 1500mg/day.
Additionally, it promotes intake of foods rich in potassium, calcium, magnesium, and fibre.
Your healthcare provider can advise on recommended servings available on the DASH Guideline which should be tailored to your dietary needs.
DASH also limits alcohol consumption since alcohol can increase blood pressure. Men are limited to no more than 2 drinks/day while women to no more than 1 drink/day. Where "a drink" refers to one glass.
Foods available on the DASH Guideline are low in sodium to ensure low-salt intake.