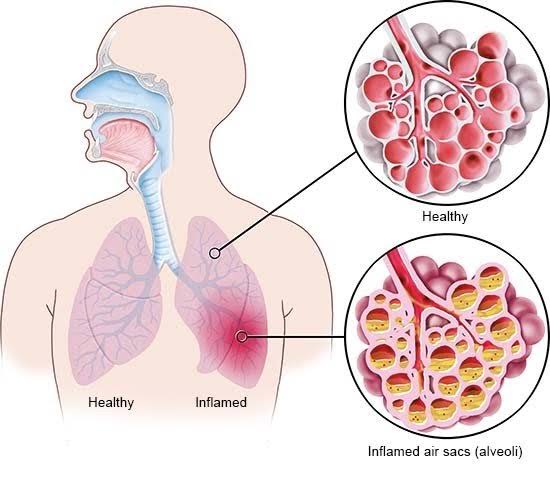
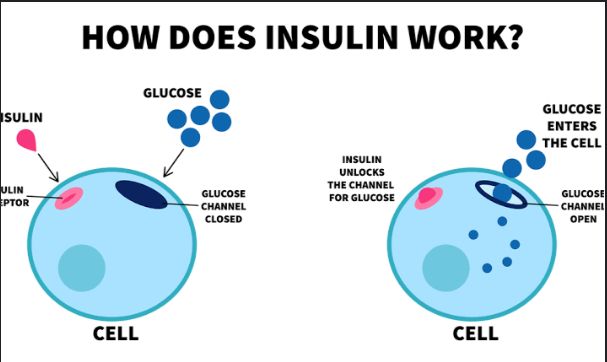
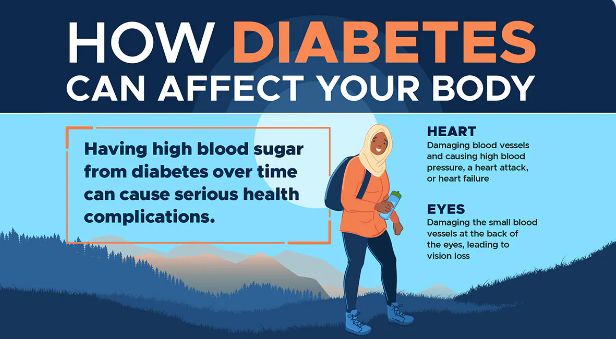
What are Congenital Heart Defects?
Congenital heart defects (CHDs) are structural abnormalities of the heart present at birth. While not all CHDs can be prevented, certain measures can reduce the risk of occurrence.
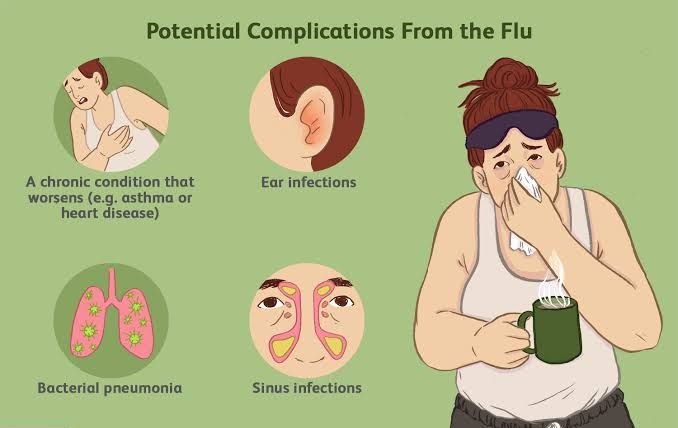
For individuals living with CHDs, effective management and care strategies are essential to maintain heart health and prevent complications.
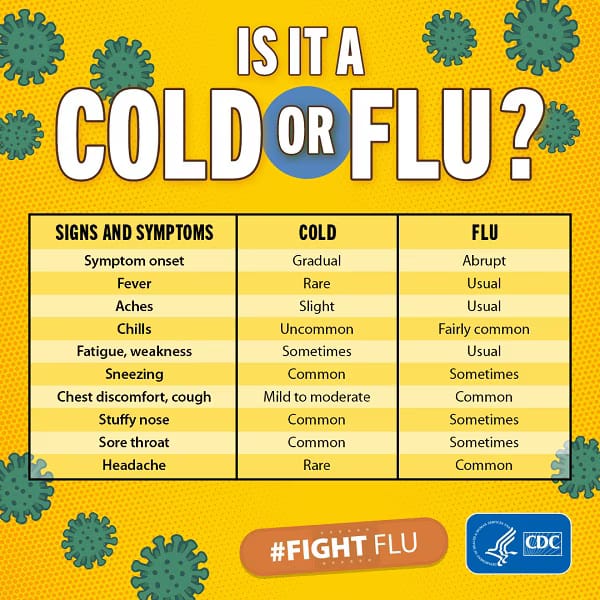
Prevention Strategies
Mainly involve Prenatal Care practices such as:
●Rubella Vaccination: Ensure vaccination against rubella before pregnancy, as contracting rubella during pregnancy can lead to CHDs in the baby.
●Folic Acid Supplementation: Taking folic acid supplements before conception and during early pregnancy can help prevent heart defects.
Also, Healthy Lifestyle Choices During Pregnancy can help reduce risk of CHD births. Practice the following:
●Avoid Harmful Substances: Refrain from smoking, alcohol consumption, and illicit drug use during pregnancy, as these can increase the risk of CHDs.
●Manage Chronic Conditions: Properly manage conditions like diabetes and hypertension under medical supervision to reduce risks.
Management and Care for Individuals with CHDs
●Regular Medical Follow-Up
Maintain routine appointments with a cardiologist experienced in congenital heart conditions to monitor heart health.
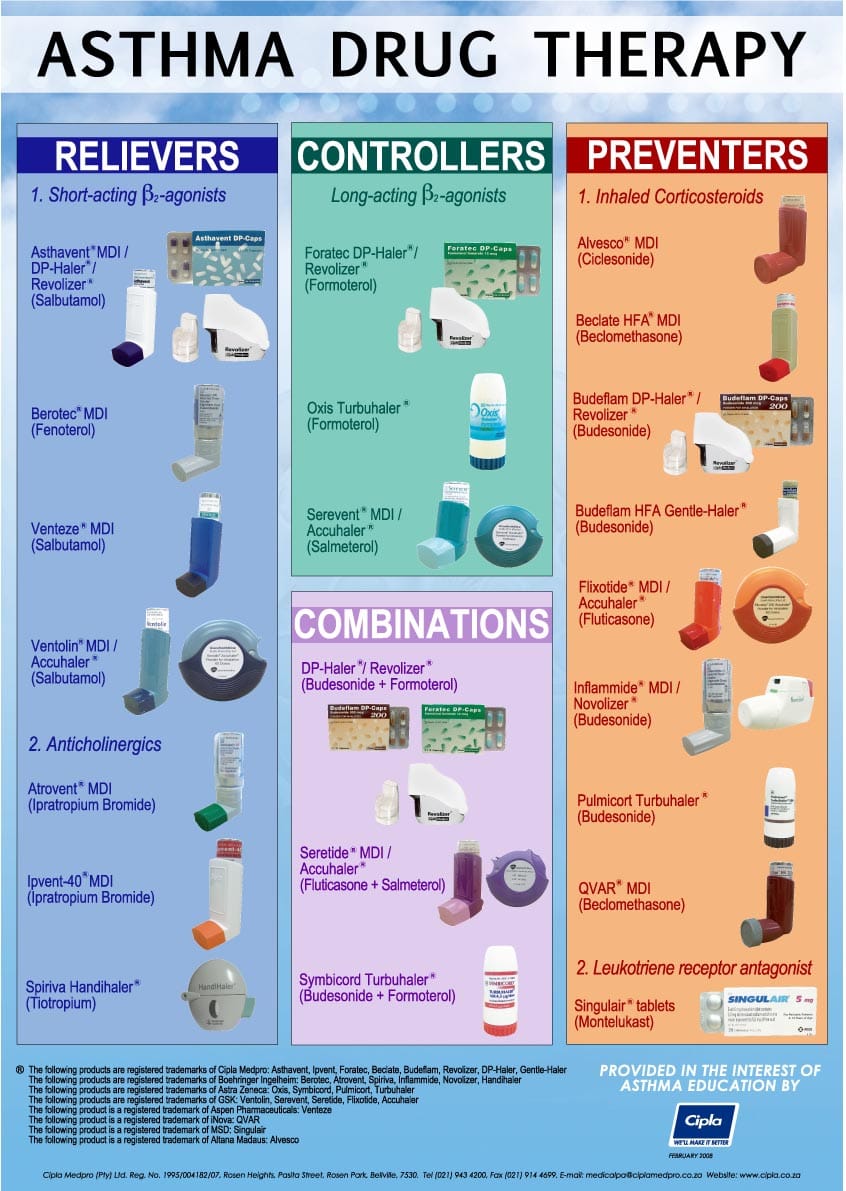
Medication Adherence: Take prescribed medications consistently to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
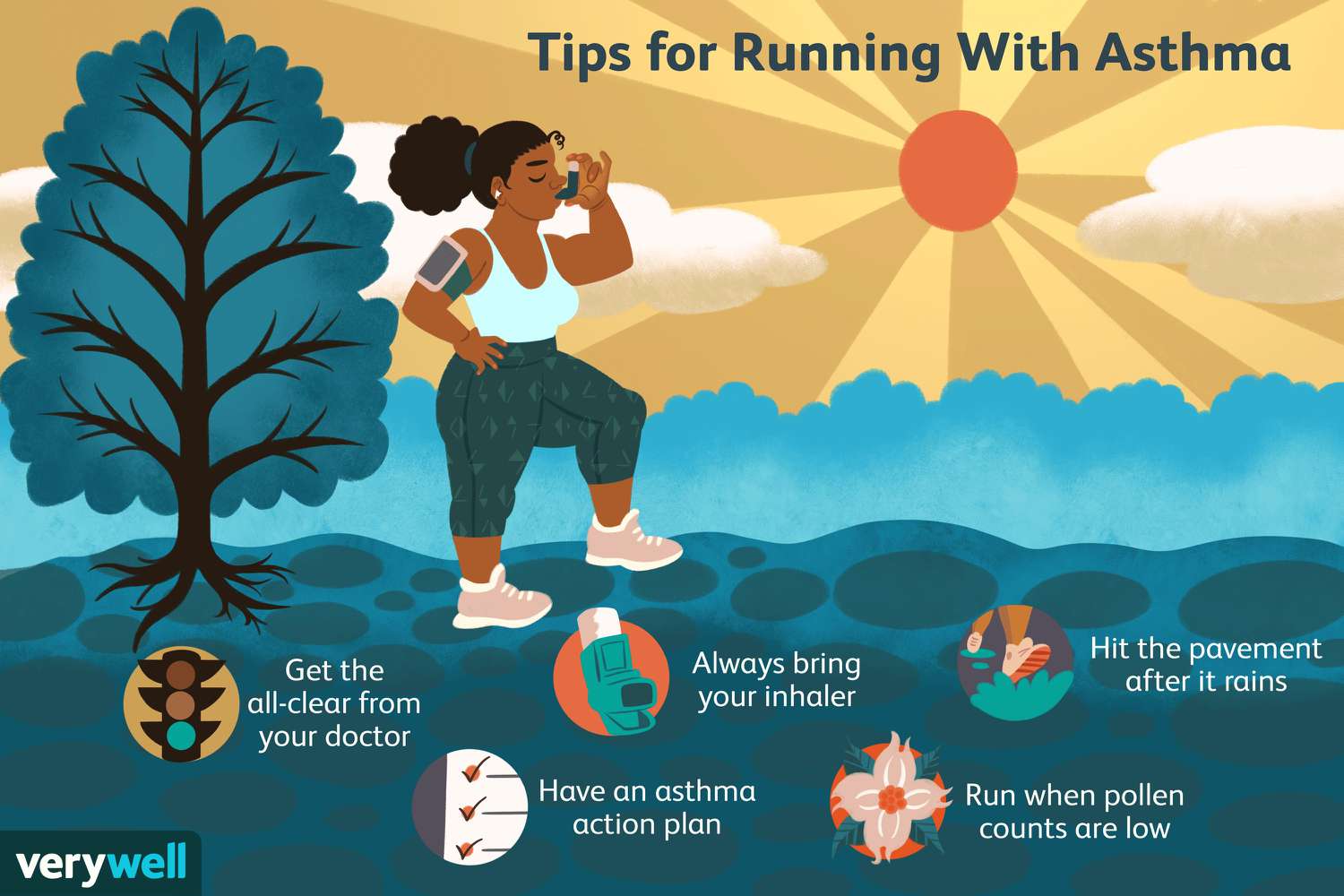
●Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Take Heart-Healthy Diet: Consume a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy products. Limit intake of saturated fats, trans fats, cholesterol, sodium, and added sugars.
Engage in Regular Physical Activity: Engage in appropriate physical activities as recommended by your healthcare provider. Exercise can improve overall cardiovascular health.
Avoid Tobacco: Do not smoke or use tobacco products, and avoid exposure to secondhand smoke.
●Infection Prevention
Hygeine: Practice proper Hygiene
Vaccinations: Stay up-to-date with vaccinations, including the flu vaccine and pneumococcal vaccine, to prevent infections that could lead to complications.
●Mental Health Support:
Seek support from mental health professionals to address feelings of anxiety or depression that may arise from living with a CHD.
Participate in support groups to connect with others facing similar challenges, which can provide emotional support and practical advice.
●Assist individuals to transition appropriately to Adult Care and Self management by:
Educating them about their condition, medications, and medical history to prepare them.
Encourage adolescents to take an active role in their healthcare, such as scheduling appointments and understanding their treatment plans.