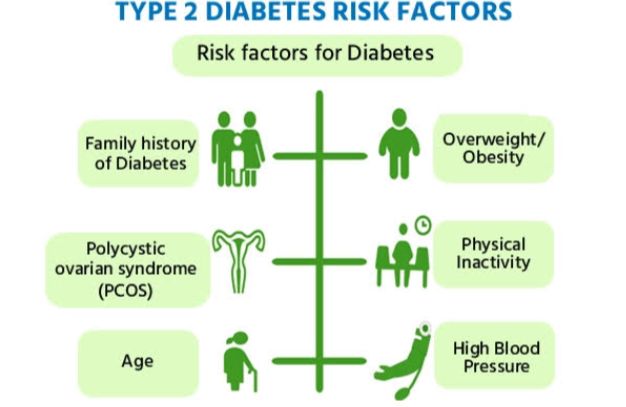
Overview of Diabetes: What is Diabetes?
•Diabetes mellitus is a disease characterized by either relative or absolute insulin deficiency leading to hyperglycemia (increased glucose levels in the blood).
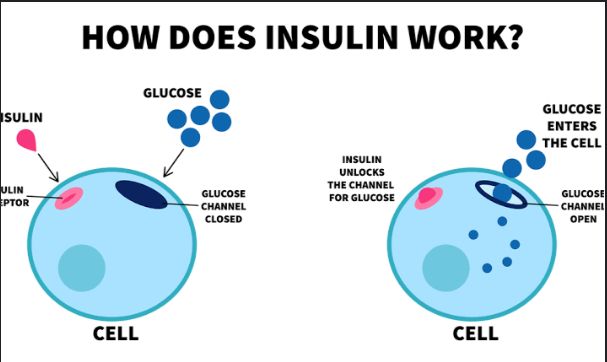
•Insulin is the hormone, produced by the beta cells of the pancreas, that helps regulate blood sugar levels.
•Diabetes is a metabolic syndrome which occurs when your body can not properly regulate blood sugar levels as a result of the inability to produce enough insulin or inability to utilize insulin effectively.
•Glucose which mainly comes from foods rich in carbohydrates is required by the body to produce energy. The body cells require insulin to absorb and utilize glucose. Therefore, when the body can not produce enough insulin or utilize insulin correctly, glucose accumulates in the bloodstream leading to hyperglycemia, a characteristic of diabetes.
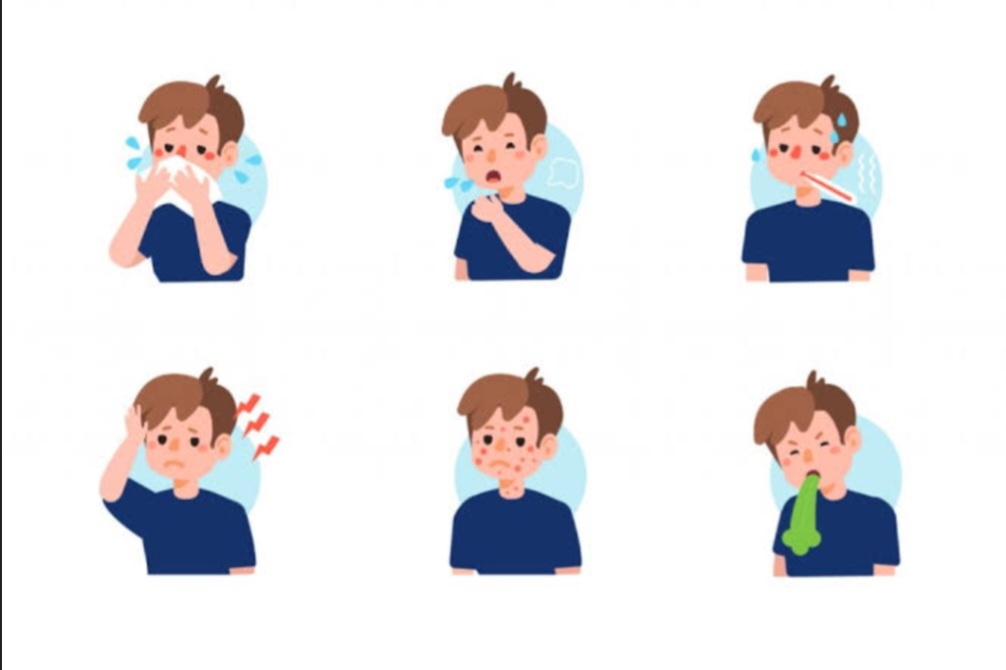
Common signs and symptoms and how to recognize them.
•Many individual have undiagnosed diabetes and only realize when they develop complications.
•The early warning signs for Diabetes are generally known as the 4Ps:
- Polyuria-Frequent urination due to osmotic pull of glucose in urine
- Polyphagia/Dysphagia- Hunger that occurs frequently since the body is unable to utilize glucose.
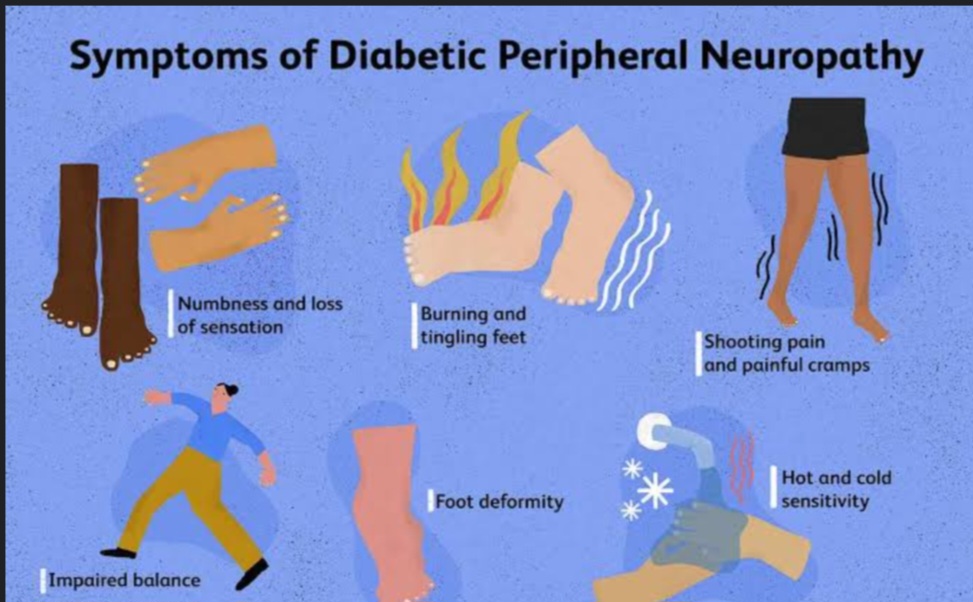
- Peripheral Neuropathy- peripheral nerves are affected. Mostly felt as burning sensation in lower limbs.
- Polydipsia- Excessive thirst leading to excessive water intake due to polyuria.
N/B: Other major signs include:
- WASTING (unexplained weight loss). Wasting can occur due to the tendency of the body to generate glucose from fats and proteins (Gluconeogenesis) or breakdown of fat in adipose tissues and muscle.
- Persistent weakness and fatigue. Occurs as a result of the inability to supply the body with enough glucose for energy.
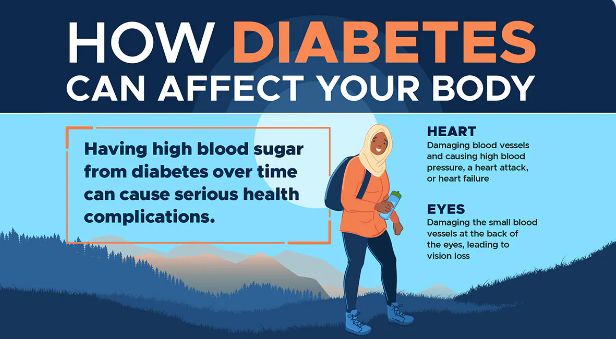
- Poor or blurred vision. If you experience sudden vision changes it is advisable to get checked for diabetes. Hyperglycaemia may lead to damage of blood vessels that supply the eye or cause changes in fluid levels in the eye.
- Slow healing wounds and cuts. High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and nerves hence leading to poor blood circulation. As a result, there is poor supply of oxygen and nutrients to tissues hence impairing healing of wounds and cuts.
- Susceptibility to infections which may depict as repeat infections
Types of Diabetes
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
In Type 1 Diabetes, the Beta pancreatic cells have been destroyed hence there is total insulin deficiency or very little production of insulin.
It is also called insulin dependent diabetes (can only be treated with insulin).
It has low prevalence (less common).
It is called Juvenile onset diabetes since it comonly begins from age 0 to 15 years, and in young adults.
Type 1 Diabetes has no genetic predisposition (not inherited). It can be caused by autoimmune disease triggered by infection.
Hyperlipidemia (increased levels of Low Density Lipids and reduced levels of High Density Lipids) is rare in type 1 Diabetes.
The hyperglycemic coma that is associated with type 1 diabetes is DKA (Diabetic keto acidosis) which has acute life threatening consequences.
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Type 2 diabetes is highly prevalent (most common type of diabetes).
It mostly occurs in adults after the age of 40 years or in rare cases you can have early onset type 2 Diabetes before the age of 40years.
It involves reduced functioning of Beta cells which causes relative insulin deficiency.
In some patients, the body may become resistant to insulin hence the insulin levels become elevated as the body tries to respond to reduced tissue sensitivity to insulin.
Due to these, type 2 Diabetes is also known as non-insulin dependent diabetes hence Oral Hypoglycemic Agents are normally used to manage it.
Type 2 Diabetes has high genetic predisposition (can be inherited).
Hyperlipidemia is common in type II Diabetes.
The hyperglycemic coma common for type 2 Diabetes is the Non-ketotic Hyperosmolar Diabetic coma (HODC) which also has acute life threatening consequences.
- Secondary Diabetes
This type of Diabetes has no pancreatic involvement.
It can be caused by endocrine disease or medications that cause hyperglycemia.
Such categories of medications include; Glucocorticoids, Oral Contraceptives, ARVs, Anti-hypertensives.
- Gestational Diabetes
Occurs in the last trimester of pregnancy for some women.
Normally occurs in about 4% of pregnancies.
It is caused by placental hormones that reduce tissue sensitivity to insulin.
It can also be caused by elevated estrogen levels during pregnancy.
Generally, gestational diabetes resolves or disappears after pregnancy.
However, women who experience gestational diabetes are at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.